HISTORY
Egyptian civilization developed and the principles of a “central government” emerged around the year 3200 BC. Where King Mines unified the Egyptian kingdoms of the north and south. The era of this state witnessed a comprehensive renaissance in various aspects of life, as the Egyptians reached the hieroglyphic writing, meaning the sacred inscription, and Memphis was established as the first capital of the country, and the kings cared about securing the borders of the country and the trade movement between Egypt and Sudan was active. Egypt received a prosperous era in its history known as the era of the pyramid builders. This era witnessed the building of the first pyramid in Egypt and the world, which is the Step Pyramid of Djoser known as the Pyramid of Saqqara, which is the first stone structure in the world and was erected in the year 2861 BC. With the development of art, agriculture and industry, the Egyptians used the first land river fleet to transport their products. Maritime navigation reached a great level. It became an organized craft like other well-established crafts that ancient Egypt was famous for, and in this era families ruled from the Third Dynasty to the Sixth Dynasty.
The Pharaohs played ball before 3000 BC, and they had competitions in which the winning team was crowned with two carats of gold.


The era of the modern state
(1580 – 1150 BC) After King Ahmose I eliminated the Hyksos and expelled them outside the borders of the eastern state of Egypt, security and stability returned to all parts of the country · Egypt began a new era, which is the era of the modern state, and Egypt realized the importance of military force to protect the country, so a strong army was established To form a great empire that stretched from the Euphrates River in the east to the fourth cataract on the Nile in the south · Egypt thus became the first superpower in the history of mankind, and thus became a great, sprawling empire and the oldest empire in history · The kings and queens of the Eighteenth Dynasty won world fame in the fields of politics and war Culture, civilization and religion · Ahmose, the hero of liberation, Amenhotep the First, the Just, who issued a law banning forced labor and setting fair standards for wages and incentives · · Thutmose I, the warrior who expanded the Egyptian borders north and south, spread education and expanded the opening of mines and the mining industry · · Thutmose II, the dandy, and Thutmose III, the emperor of genius The military feat and the first great conqueror in the history of the world · · Tuthmosis IV the diplomat who was the first to be interested in codifying and recording international treaties · · and Amenhotep III the richest king in the world The old one who opened the schools «Houses of Life» to spread education and plastic and applied arts ··
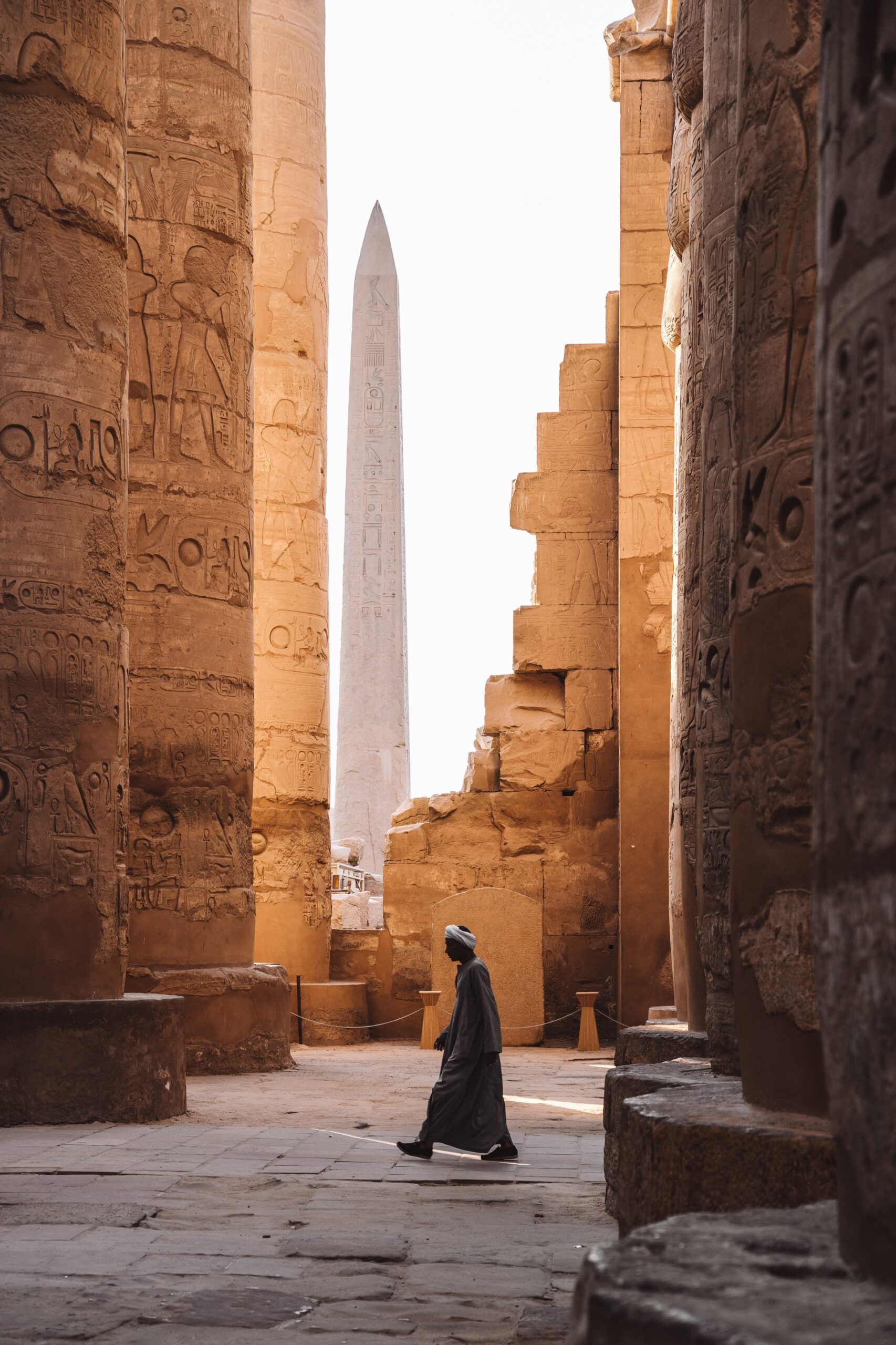
And Akhenaten was the first to call for the unification of the Pharaonic gods and symbolize them with the disk of the sun · · And Tutankhamun, who won fame in the contemporary world · Among the most famous queens of this family, for example, Queen Iahhotep, wife of King “Saqnen Ra”, and Queen “Ahmose-Nefertari”, wife of Ahmose I , and Queen T, the daughter of the people, the wife of Amenhotep III and the mother of Akhenaten, and Queen Nefertiti, the wife of Akhenaten, and the great Queen Hatshepsut, who ruled Egypt for nearly twenty years. During her reign, Egypt reached the highest summit in civilization, architecture and international trade, as it sent the commercial and scientific marine mission to the country of “Punt” and also built one One of the greatest, most splendid and luxurious architectural monuments is the temple of “Deir el-Bahari” on the western shore of the Nile in front of Luxor. It is a unique temple in its design and has no equal among all the temples of the ancient world, and the Karnak Temple, which is the largest temple in the ancient world. This era also witnessed the “Akhenaten Revolution.” Religious »where he called for the worship of one god and symbolized him with the disk of the sun and established a new capital for the country and called it «Akhitaten» · And King Ramesses II who defeated the Hittites and concluded with their king the first peace treaty in history and built about 6 temples, the most famous of which is the Temple of Ab And Sembel, and Ramses III, who repelled the attacks of the Libyans and the peoples of the Mediterranean
Middle Kingdom era
The Middle Kingdom (2040 – 1640 BC) precedes the first middle age, in which dynasties ruled starting from the seventh to the tenth, which ended with the division of the country, to come the era of the Middle Kingdom, which began with Pharaoh Mentuhotep II in 2065 BC, who was a prince of Thebes and reunified the country He imposed order, and the kings of the Middle Kingdom took care of the most beneficial projects for the people, so agriculture flourished and handicrafts developed, and Egyptian artists and engineers produced a wonderful heritage that spread in Luxor, Fayoum and Ain Shams The state The second middle age, in which the families ruled from 13 to 17, and in which the middle state weakened, and this led to the raiding of tribes inhabiting the eastern Mediterranean region, known as the Hyksos, to Egypt, and their invasion of regions in the north and center of the country.

Persian invasion of Egypt
After Cambyses II, son of Cyrus the Great, assumed the throne, he worked to establish the foundations of his rule and secure his borders, in which some unrest arose, and after four years he began to think of occupying Egypt and annexing it to the Persian Empire. Cambyses II asked for the hand of Ahmose II’s daughter, but he refused and decided to send him the daughter of King Abris instead of her, which made Cambyses very angry and accelerated his occupation of Egypt.
During the reign of Ahmose II, Egypt enjoyed great progress and stability throughout his reign. Despite this, there were some weaknesses that seemed to pose a danger, including that the Egyptian army was the mainstay of many foreign mercenary elements, which makes their loyalty questionable, as well as the grants that belonged to them. Ahmose made them the subject of envy and hatred of the Egyptians, and it was as a result of those things that one of the leaders in the army, called Fanis, fled to the ranks of the army of Cambyses and told him about the plans of the Egyptian army and its locations, as he showed him the paths of the desert.
Ahmose tried to prepare for the expected attack by Cambyses by trying to conclude an alliance with the country of Cyprus and the tyrant Polycrates of Samos, who had a large fleet in order to have maritime sovereignty, but he failed as he let him down and joined the Persians.
Cambyses was able to secure water for his army from the leaders of the regions that his army would pass through in the southern desert, and in the meantime, Ahmose II died before Cambyses began his campaign and reached Egypt, and his son Psamtik III assumed power to succeed his father. Pelusium borders near Port Said, and Psamtik was defeated in that battle and withdrew to Memphis, and Cambyses continued his progress, reaching Ain Shams and then to Memphis, where he faced Psamtik again, but he was defeated and captured in this battle and Cambyses seized the capital, and Egypt became a Persian state

Greek era
Alexander the Macedonian succeeded in defeating the Persians in Asia Minor and continued his conquests as far as India, where he sought the help of a naval team and Egyptian exploratory crews, and before that he succeeded in expelling the Persians from Egypt who did not resist the year 333 BC. Alexander crowned himself king on the path of the Pharaohs and laid the foundation of the city of Alexandria, then made a pilgrimage to the Temple of Amun in the Siwa Oasis, which enjoyed wide international fame at that time.
The rule of the Ptolemies is the dynasty that descended from Ptolemy, one of Alexander’s close leaders, Egypt from 333 until 30 BC, when 15 Ptolemaic kings took over the rule of Egypt. The independence of Egypt, where Rome sought to extend its influence over Egypt and eliminated the Ptolemies in the year 30 BC during the reign of Queen Cleopatra VII, who was the last king of Ptolemaic Egypt and ended Egypt’s independence and joined the Roman Empire.


Aspects of Egyptian civilization during the Ptolemaic era
The Ptolemies built palaces and gardens in Alexandria, and Alexandria became a center of civilization, as it became famous in the field of art, science, industry, and trade. It was also the first port in the Mediterranean thanks to its famous lighthouse, which the Greeks considered one of the Seven Wonders of the World.
A great Greek civilization was established in Alexandria, represented in:
The (old) University of Alexandria, which was established by the Ptolemies, thanks to the scholars of the University of Alexandria in reaching scientific facts about the Earth’s rotation around the sun and estimating the circumference of the globe. The geographer and the Egyptian historian Manetho
The Library of Alexandria and its cultural impact: The Ptolemies established in Alexandria a huge library that was considered the greatest library in the world and contained more than half a million papyrus scrolls. ·
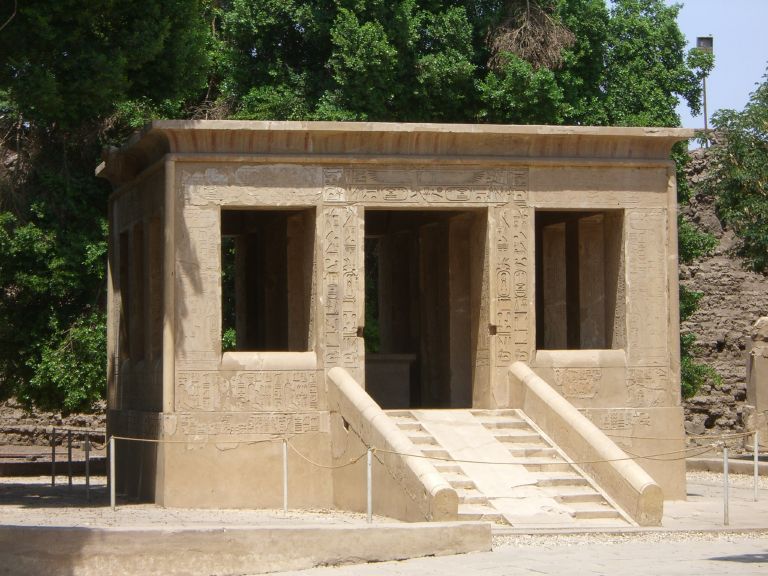
The Ptolemies respected the religion of the Egyptians and made offerings to Egyptian deities, and built temples for them such as the Edfu Temple, the Dendera Temple and the Philae Temples in Aswan.
Ptolemy I annexed to Egypt a number of annexes, namely Cyrenaica, southern Syria, Phenicia, Palestine and Cyprus.
Greek era
The Romans entered Egypt in the year 30 B.C. and it became one of its provinces. Indeed, Egypt became one of the most important provinces of the Roman Empire due to its economic importance.
The manufacture of glass, paper and linen, in addition to perfumes and cosmetics, was also famous in Egypt.

Coptic era
Christianity entered Egypt in the middle of the first century AD, when Saint Mark entered Alexandria and established the first church in Egypt and Africa as a whole.
Christians suffered from persecution by the Romans, especially during the period of Emperor Diocletian, who made the Copts from the year of his ascension to the throne of the empire the beginning of the annual calendar for Coptic Christians.
The world learned different aspects of Coptic literature, the most important of which are the sayings of the fathers, then the sermons of the saints in the struggle of paganism to establish Christianity, then magic, then worldly or popular literature. As for the sayings of the fathers, they are the ecclesiastical sayings that supported monasticism and showed its psychological and practical aspects. Delegations to Egypt from the east and west wrote down these sayings and proved them in their Greek, Latin and Syriac languages. The Coptic monks in their early ages were known for their piety and humility, so they used to work and teach. Their sayings came in different languages in the Book of the Monks’ Garden and in the books of the fathers who are skilled in worship as well as in their lives. Coptic saints appeared in Egypt who the world did not know were stronger than them in establishing Christianity and striving against paganism.
Islamic era
Islam entered Egypt during the reign of the Arab caliph Umar ibn al-Khattab and under the leadership of Amr ibn al-Aas in the year 641 AD. During the period of Arab Islamic rule, Egypt witnessed progress in the areas of urbanization and the arts, such as architecture, decorations and inscriptions of Islamic style, and many mosques, castles and walls were built.
And in the Fatimid era, the Al-Azhar Mosque was considered the most famous architecture during the era of the Fatimid Caliphate in Egypt, in addition to several other aspects. Salah al-Din Citadel, which is the most famous castle in Cairo, in addition to the architectural wealth that appeared during the Mamluk era.

upper family
Muhammad Ali is considered the founder of modern Egypt because of the reforms he carried out that included all aspects of life in accordance with the spirit of the modern era at the time. He began building Egypt’s strong army and established the Military School. Shipbuilding was established in Bulaq and the naval arsenal in Alexandria. He reformed the conditions of agriculture and irrigation, established barrages, dams, and canals, and established factories and laboratories to meet the needs of the army and sell the surplus to the people. In the field of trade, Muhammad Ali Pasha worked to spread security for internal trade routes, and he established a fleet for foreign trade, as trade flourished in Egypt.
He spread education to meet the needs of government offices, so he established schools of all levels and specializations, and sent missions to Europe and the transfer of modern sciences.
The sons of Muhammad Ali tried to follow his path in an attempt to catch up with European civilization. During the reign of Khedive Ismail Pasha, the country witnessed a renaissance represented in administrative reform. Industry and agriculture also witnessed a great renaissance and prosperity during his reign. He was interested in building and architecture, and he established the Khedive Opera House, laying railways, and in The year 1869 opened the Suez Canal for international navigation in a great celebration.
Egypt witnessed several revolutions against foreign interference, as the national movement intensified. It was the Urabi Revolution in 1882, which ended with the British occupation of Egypt, which declared protection over Egypt in 1914 and ended its official subordination to the Ottoman Empire.

The first republic
Egypt entered the twentieth century burdened by the burdens of British colonialism, with its pressures to plunder its wealth, and the popular resistance and national movement against the occupation escalated under the leadership of Mustafa Kamel and Muhammad Farid. Egypt in 1922 and the recognition of its independence and the first Egyptian constitution was issued in 1923.
The era of the revolution
Al-Bakbashi Gamal Abdel Nasser, Major General Muhammad Naguib, and other Egyptian Free Officers led the revolution of July 23, 1952. It carried out many tasks, the most important of which was the issuance of the Agrarian Reform Law, and the first five-year plan for economic and social development in the history of Egypt in 1960, and an attempt to develop industry and production, and the High Dam was established. 1960-1970, which is considered by the United Nations to be the most important development project in the world in the twentieth century. In order to complete its construction, Egypt fought a long war against the great powers that wanted to rein in Egypt during the rule of Gamal Abdel Nasser. It also assisted the country in the field of education, health, construction, reconstruction, and agriculture. . In the field of foreign policy, the July Revolution, led by Gamal Abdel Nasser, encouraged liberation movements from colonialism. It also took the policy of positive neutrality as a basic principle in its foreign policies. During that period, Egypt became the capital of national liberation in the world. Israel, France and England made an organized attack on Egypt, while It was called the tripartite aggression against Egypt, and the Egyptian army and the popular resistance carried out heroic deeds to repel the French and the British. As for Israel, it took Sinai completely, but a decision was issued by the Security Council at that time to return all the occupied lands to Egypt and the illegality of the attack on Egypt.
On June 5, 1967, Israel launched an attack on Egypt, Syria, and Jordan, and occupied Sinai, the Golan Heights, and the West Bank of Jordan.
Despite the enormity of the loss, the Egyptian army was able to pass this ordeal in its steadfastness in front of the Israeli forces and its entry into the war of attrition. At that time, Gamal Abdel Nasser died in September 1970, and his funeral was one of the largest funerals in history.

October War
Muhammad Anwar Sadat assumed power after Gamal Abdel Nasser. He worked to settle the internal problems of the state and prepare Egypt to wage a war to liberate the Sinai. On October 6, 1973, at exactly two o’clock in the afternoon, the Egyptian armed forces and the Syrian Arab armed forces carried out an attack on the Israeli forces in both the Sinai Peninsula and the Golan Heights. The war on the Egyptian front began with the air strike launched by the Egyptian Air Force against the Israeli forces, and the Egyptian forces crossed to the eastern bank and raised the Egyptian flag.
President Anwar Sadat entered into a settlement of the Arab-Israeli conflict to find an opportunity for lasting peace in the Middle East region, so he agreed to the peace treaty presented by Israel (Camp David) on March 26, 1979 with the participation of the United States after President Sadat’s visit to Israel paved the way in 1977, and Israel withdrew from the semi-autonomous Sinai Island completely on April 25, 1982 with its withdrawal while retaining the Taba border strip, and the Egyptian government later recovered this strip, based on the arbitration that took place in the International Court of Justice later.
Egypt’s signing of the peace agreement and Sadat’s visit to Israel sparked resentment inside and outside Egypt. Supporters of this agreement believe that it returned Sinai to Egypt and paved the way for peace in the Middle East. While its opponents believe that the effects of this agreement is that it isolated an Arab country that has political and military weight, namely Egypt, from the Arab-Israeli conflict, and worked to limit the scope of the Egyptian army’s movement in the Sinai, and it also weakened Egypt’s leading role in the Arab world. On November 2, 1978, a conference of the League of Arab States was held, in which it was decided to transfer the headquarters of the League of Arab States from Egypt, and suspended Egypt’s membership from 1979 to 1989. Ten Arab countries participated in this summit in addition to the Palestine Liberation Organization, and the United Arab Emirates opposed the Arab steps against Egypt.
Sadat’s assassination
By the fall of 1981, the government carried out a massive campaign of arrests that included heads of Islamic movements, Coptic Church officials, writers opposed to President Sadat, journalists, leftist and liberal thinkers, and the number of detainees in Egyptian prisons reached 1,420, following the occurrence of signs of strife and popular unrest rejecting reconciliation with Israel and the state’s economic policies. President Sadat intends to release them as soon as he receives the land of Sinai.
On October 6, 1981 (31 days after the arrest warrants were announced), Sadat was assassinated in a military parade that was taking place on the occasion of the anniversary of the October War. The organization carried out by the government in September. His successor in the presidency was Vice President Mohamed Hosni Mubarak.
Mubarak era
= October 14, 1981 Muhammad Hosni Mubarak assumed the presidency of the Arab Republic of Egypt, after the People’s Assembly nominated him.
= October 5, 1987 he was re-nominated as President of the Republic for a second term.
= 1993 He was re-nominated as President of the Republic for a third presidential term.
= September 26, 1999, he was re-nominated as President of the Republic for a fourth presidential term.
= He was also elected for a new term in 2005 in the first pluralistic presidential elections in Egypt, following a constitutional amendment.

The second republic
On January 25, 2011, a popular revolution took place, known as the January 25 Revolution. The protests lasted for 18 days, and on February 11, Muhammad Hosni Mubarak announced his resignation and assigned the Supreme Council of the Armed Forces to manage the country’s affairs. Egypt began a phase called the democratic transition phase. A referendum was held to amend the 1971 constitution, which included limiting presidential terms to only two terms. Then elections were held for the People’s Assembly and the Shura Council. On June 21, 2012, Mohamed Morsi was declared president of the republic after multiparty presidential elections in which 13 candidates participated.
Mohamed Morsi’s presidency of Egypt lasted one year, as demonstrations took place on June 30, 2013, and the Armed Forces, led by Defense Minister Abdel Fattah El-Sisi, carried out a coup deposing the president and replacing him with Adly Mansour as interim president. Supporters of the ousted president gathered in two important squares in Cairo and Giza for 65 days, then their sit-in was dispersed, and this process and its consequences left hundreds dead.
After a transitional period of one year, presidential elections were held, in which only two candidates were nominated: Defense Minister Abdel Fattah El-Sisi and Hamdeen Sabahi. Al-Sisi was declared the winner of the presidency of Egypt, with a rate of 96.1%.
